
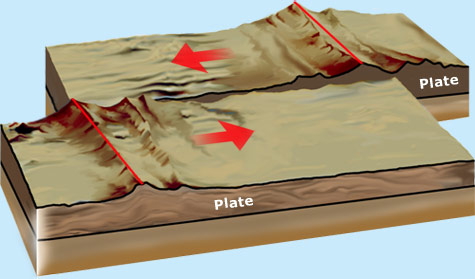
What is Transform plates?Transform plates are plates that slide past each other this movement results in the formation of a transform fault in the process tremendous stress builts up and its eventually release often in the form of violent earthquakes 2. The proof of this is found in paleo-magnetic striping on the sea floor. California’s sheared-up landscape and earthquake hazards reflect the movement. The San Andreas Fault is the transform plate boundary where a. Instead of the ridges moving away from each other, like other strike-slip faults, transform fault ridges will stay in the same fixed location, and the new ocean sea floor being created at the ridges is pushed away from the ridge. Transform Plate Boundaries NPS Landscapes Developed at Transform Plate Boundaries. Transform faults move differently than a strike-slip fault at the mid-oceanic ridge. Transform faults show up on the seafloor as valleys that may be even deeper than the rift valleys of spreading ridges. Transform faults are the only type of strike-slip fault that can be classified as a plate boundary. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. transform fault, in geology and oceanography, a type of fault in which two tectonic plates slide past one another. Most transform faults are found in the ocean where they offset.
#At transform plate boundaries series#
Most transform faults are hidden in the deep oceans where they form a series of short zigzags accommodating seafloor spreading, the best-known (and most destructive) are those on land at the margins of tectonic plates. A transform fault or transform boundary, sometimes called a strike-slip boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. A transform boundary is a fault zone where two plates slide past each other horizontally. Other locations include: the East Pacific Ridge located in the South Eastern Pacific Ocean, which meets up with San Andreas Transform fault to the North. Paul, Romanche, Chain, and Ascension fracture zones, these areas have with deep, easily identifiable transform faults and ridges. Locations of transform plate boundary:transform zones are located in Atlantic Ocean between South America and Africa. Take a ten question quiz about this page.Transform Plate Boundary by Bt Mawar Malyanah 1.

It is the cause of so many earthquakes in California. It is the boundary between the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is released as seismic waves, causing the ground to shake. As the plates move past each other, they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up. One famous transform boundary is the San Andreas Fault in California. Most seismic activity occurs at three types of plate boundariesdivergent, convergent, and transform.These places are often called faults and can be areas where earthquakes often occur. Transform Boundaries - A transform boundary is one where two plates slide past each other.New land is formed by magma pushing up from the mantle and cooling as it reaches the surface. The area on land where the boundary occurs is called a rift. Earthquakes are generated along this type of. Divergent Boundaries - A divergent boundary is one where two plates are getting pushed apart. (Figure 4c): occur where two lithospheric plates slide laterally past each other.Here is a picture showing the major tectonic plates of the world. Some of the minor plates include the Arabian, Caribbean, Nazca, and Scotia plates. The seven major plates include the African, Antarctic, Eurasian, North American, South American, India-Australian, and the Pacific plates. Most of the Earth is covered by seven major plates and another eight or so minor plates. Some of these plates are huge and cover entire continents. The lithosphere moves in big chunks of land called tectonic plates. The lithosphere is made up of the Earth's crust and a part of the upper mantle. The part of the land that is moving is the Earth's surface called the lithosphere. The locations of earthquakes along mid-ocean ridges, and the. It takes millions of years for the land to move a significant amount. Mid-ocean ridge divergent plate margins are offset by numerous transform faults (Figure 12.17). This movement is way too slow for us to notice, however, because it only moves between one to 6 inches per year. Although we think of the land on Earth as being fixed and stable, it turns out that it is constantly moving.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
